|
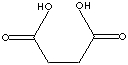
SUCCINIC ACID |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 110-15-6 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 203-740-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | HOOCCH2CH2COOH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 118.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE |
2917.19 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 2260 mg/kg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Butanedionic acid; Amber acid; Butanedioic acid; | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dihydrofumaric acid; asuccin; 1,2-ethanedicarboxylic acid; wormwood; wormwood acid; katasuccin; Asuccin; Bernsteinsaure (German); Kyselina Jantarova (Czech); | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RAW MATERIALS |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Succinic Acid (Butanedioic Acid) is a dicarboxylic acid of four carbon atoms. It occurs naturally in plant and animal tissues. It plays a significant role in intermediary metabolism (Krebs cycle) in the body. Krebs cycle (also called citric acid cycle; tricarboxylic acid cycle) is a sequence process of enzymatic reaction which a two-carbon acetyl unit is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water to provide energy in the form of high-energy phosphate bonds. Succinic acid is a colourless crystalline solid with a melting point of 185 -187 C; soluble in water; slightly dissolved in ethanol, ether, acetone and glycerine; not dissolved in benzene, carbon sulfide, carbon tetrachloride and oil ether. The common method of synthesis of succinic acid is the catalytic hydrogenation of maleic acid or its anhydride. Carboxylic acid can yield acyl halides, anhydrides, esters, amides, and nitriles for the application of drug, agriculture, and food products, and other industrial uses. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Odorless white crystals | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 187 - 189 C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 235 C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.552 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
moderately soluble |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 3.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
630 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
1.405 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
206 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPLICATIONS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Flavoring agent for food and beverages; Producing five heterocyclic compounds, Intermediate for dyes, perfumes, lacquers, photographic chemicals, alkyd resins, plasticizer, Metal treatment chemical, vehicle water cooling systems and coatings. Medicines of sedative, antispasmer, antiplegm, antiphogistic, anrhoter, contraception and cancer-curing. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
Colorless to white crystalline power |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PURITY |
99.50% min |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FUMARIC & MALEIC ACID |
0.1% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT |
185 - 189 C |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CHLORIDE (Cl ) |
0.002% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
IRON (Fe ) |
0.002% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SULFATE ( SO4) |
0.002% max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ARSENIC ( As ) |
3ppm max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
HEAVY METAL (As Pb ) |
10ppm max |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dicarboxylic
acid is a compound containing two carboxylic acid, -COOH,
groups. Straight chain examples are shown in table. The
general formula is HOOC(CH2)nCOOH,
where oxalic acid's n is 0, n=1 for malonic acid, n=2 for succinic acid, n=3
for glutaric acid, and etc. In substitutive
nomenclature, their names are formed by adding -dioic'
as a suffix to the name of the parent compound. They
can yield two kinds of salts, as they contain two carboxyl
groups in its molecules. The range of carbon chain lengths is from 2, but the
longer than C 24 is very rare. The term long chain
refers to C 12 up to C 24 commonly. Carboxylic
acids have industrial application directly or indirectly
through acid halides, esters, salts, and anhydride forms,
polymerization, and etc. Dicarboxylic acids
can yield two kinds of salts
or esters, as they
contain two carboxyl groups in one molecule.
It is useful in a variety of industrial applications
include;
There are almost infinite esters obtained from carboxylic acids. Esters are formed by removal of water from an acid and an alcohol. Carboxylic acid esters are used as in a variety of direct and indirect applications. Lower chain esters are used as flavouring base materials, plasticizers, solvent carriers and coupling agents. Higher chain compounds are used as components in metalworking fluids, surfactants, lubricants, detergents, oiling agents, emulsifiers, wetting agents textile treatments and emollients, They are also used as intermediates for the manufacture of a variety of target compounds. The almost infinite esters provide a wide range of viscosity, specific gravity, vapor pressure, boiling point, and other physical and chemical properties for the proper application selections.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||